DQN 神经网络 (Tensorflow)
学习资料:
要点 ¶
接着上节内容, 这节我们使用 Tensorflow (如果还不了解 Tensorflow, 这里去往 经典的 Tensorflow 视频教程) 来搭建 DQN 当中的神经网络部分 (用来预测 Q 值).
两个神经网络 ¶
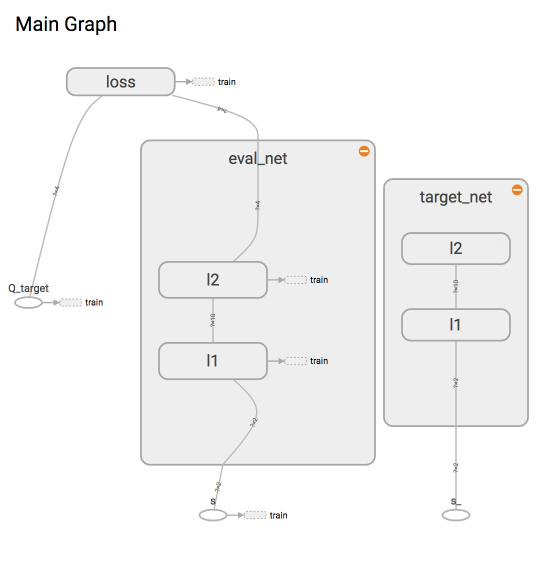
为了使用 Tensorflow 来实现 DQN, 比较推荐的方式是搭建两个神经网络, target_net 用于预测 q_target 值, 他不会及时更新参数.
eval_net 用于预测 q_eval, 这个神经网络拥有最新的神经网络参数. 不过这两个神经网络结构是完全一样的, 只是里面的参数不一样.
在这个短视频里, 能找到我们为什么要建立两个不同参数的神经网络.
神经网络结构 ¶
因为 DQN 的结构相比之前所讲的内容都不一样, 所以我们不使用继承来实现这次的功能.
这次我们创建一个 DeepQNetwork 的 class, 以及他神经网络部分的功能. 下次再说强化学习的更新部分.
class DeepQNetwork:
# 建立神经网络
def _build_net(self):
创建两个网络 ¶
两个神经网络是为了固定住一个神经网络 (target_net) 的参数, target_net 是 eval_net 的一个历史版本,
拥有 eval_net 很久之前的一组参数, 而且这组参数被固定一段时间, 然后再被 eval_net 的新参数所替换.
而 eval_net 是不断在被提升的, 所以是一个可以被训练的网络 trainable=True. 而 target_net 的 trainable=False.
class DeepQNetwork:
def _build_net(self):
# -------------- 创建 eval 神经网络, 及时提升参数 --------------
self.s = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name='s') # 用来接收 observation
self.q_target = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_actions], name='Q_target') # 用来接收 q_target 的值, 这个之后会通过计算得到
with tf.variable_scope('eval_net'):
# c_names(collections_names) 是在更新 target_net 参数时会用到
c_names, n_l1, w_initializer, b_initializer = \
['eval_net_params', tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES], 10, \
tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.3), tf.constant_initializer(0.1) # config of layers
# eval_net 的第一层. collections 是在更新 target_net 参数时会用到
with tf.variable_scope('l1'):
w1 = tf.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_l1], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [1, n_l1], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.s, w1) + b1)
# eval_net 的第二层. collections 是在更新 target_net 参数时会用到
with tf.variable_scope('l2'):
w2 = tf.get_variable('w2', [n_l1, self.n_actions], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
self.q_eval = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2
with tf.variable_scope('loss'): # 求误差
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.q_target, self.q_eval))
with tf.variable_scope('train'): # 梯度下降
self._train_op = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(self.lr).minimize(self.loss)
# ---------------- 创建 target 神经网络, 提供 target Q ---------------------
self.s_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name='s_') # 接收下个 observation
with tf.variable_scope('target_net'):
# c_names(collections_names) 是在更新 target_net 参数时会用到
c_names = ['target_net_params', tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES]
# target_net 的第一层. collections 是在更新 target_net 参数时会用到
with tf.variable_scope('l1'):
w1 = tf.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_l1], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [1, n_l1], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.s_, w1) + b1)
# target_net 的第二层. collections 是在更新 target_net 参数时会用到
with tf.variable_scope('l2'):
w2 = tf.get_variable('w2', [n_l1, self.n_actions], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
self.q_next = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2
如果想一次性看到全部代码, 请去我的 Github
分享到:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
如果你觉得这篇文章或视频对你的学习很有帮助, 请你也分享它, 让它能再次帮助到更多的需要学习的人.
UnityTutorial没有正式的经济来源, 如果你也想支持 UnityTutorial 并看到更好的教学内容, 赞助他一点点, 作为鼓励他继续开源的动力.